In recent years, cannabidiol (CBD) has captured widespread attention for its potential health benefits. From relieving pain and anxiety to addressing neurological disorders, Cannabidiol's versatility has sparked scientific curiosity and consumer interest alike. Beneath its popularity lies a fascinating molecular dance—CBD's interaction with the endocannabinoid system and other receptor systems within the body. This article delves into the intricate science behind Cannabidiol's mechanism of action, shedding light on how it exerts its effects on various physiological processes.
Table of Contents
- 1 The Endocannabinoid System: A Primer
- 2 The ECS and Homeostasis
- 3 CB1 and CB2 Receptors
- 4 Cannabidiol and Receptor Interaction
- 5 Modulating CB1 and CB2 Receptors
- 6 Beyond Receptors: Additional Pathways
- 7 Enzymes and Enzyme Inhibitio
- 8 Prolonging Endocannabinoid Effects
- 9 Neurological Effects and Neuroprotection
- 10 Promoting Neuroplasticity
- 11 Reduction of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
- 12 Modulation of Inflammation and Immune Responses
- 13 Influencing Immune Cells
- 14 CBD and Anxiolytic Properties
- 15 Anxiolytic Potential
- 16 Analgesic Effects and Pain Management
- 17 Targeting Pain Pathways
- 18 Bioavailability and Administration Methods
- 19 Maximizing Cannabidiol Absorption
- 20 Safety, Side Effects, and Future Research
- 21 CBD's Safety Profile
- 22 Ongoing Research and Potential
- 23 Conclusion
- 24 Frequently Asked Questions
- 25 Is CBD the same as THC?
- 26 How does Cannabidiol interact with the endocannabinoid system?
- 27 What are CB1 and CB2 receptors?
- 28 Does CBD directly bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors?
- 29 Can Cannabidiol help with anxiety?
- 30 Does CBD have pain-relieving properties?
- 31 What is the entourage effect?
- 32 How is Cannabidiol metabolized in the body?
- 33 Are there any side effects of using Cannabidiol?
- 34 Is CBD legal?
The Endocannabinoid System: A Primer
The ECS and Homeostasis
Imagine a finely tuned orchestra within your body, ensuring that everything is in harmony. This symphony is orchestrated by the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids. The ECS plays a pivotal role in maintaining homeostasis, the delicate equilibrium necessary for optimal bodily function.
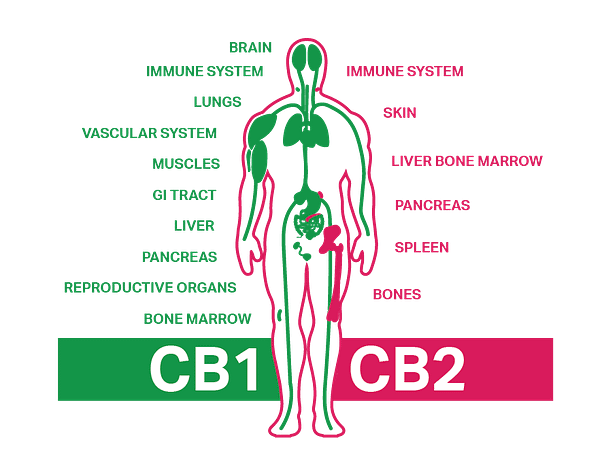
CB1 and CB2 Receptors
Central to the ECS are two main types of receptors: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are primarily nestled within the brain and central nervous system, influencing processes like memory, mood, and pain perception. On the other hand, CB2 receptors are predominantly found in immune cells, regulating inflammation and immune responses throughout the body.
Cannabidiol and Receptor Interaction
Modulating CB1 and CB2 Receptors
Unlike its cousin THC, CBD doesn't bind directly to CB1 and CB2 receptors. Instead, it acts as a subtle conductor, fine-tuning the activity of these receptors. By modulating their signaling, Cannabidiol can indirectly influence a spectrum of physiological functions, offering a delicate balance without inducing the psychoactive “high” associated with THC.
Beyond Receptors: Additional Pathways
The influence of CBD extends beyond cannabinoid receptors. Cannabidiol engages with serotonin receptors (5-HT1A), key players in mood regulation and anxiety. This interaction contributes to CBD's anxiolytic potential, suggesting its usefulness in managing stress and anxiety. Furthermore, Cannabidiol's activation of the TRPV1 receptor underscores its potential in alleviating pain and reducing inflammation.
Enzymes and Enzyme Inhibitio
Prolonging Endocannabinoid Effects

To understand CBD's mechanism fully, one must explore the realm of enzymes. Cannabidiol interacts with enzymes responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids, such as anandamide. By inhibiting these enzymes, CBD prolongs the presence and impact of these natural cannabinoids, amplifying their influence on the body's regulatory systems.
Neurological Effects and Neuroprotection
Promoting Neuroplasticity
In the intricate landscape of the brain, CBD seems to encourage neuroplasticity—an essential feature that allows the brain to adapt, rewire, and form new connections. This phenomenon has significant implications, particularly in conditions marked by neurodegeneration, as CBD's neuroprotective properties could potentially slow down the progression of diseases like Alzheimer's.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
- Antioxidant Shield: Cannabidiol dons the role of an antioxidant, safeguarding neurons from oxidative stress and potential damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Guardian: By combating inflammation, Cannabidiol contributes to overall neural health and function.
Modulation of Inflammation and Immune Responses
Influencing Immune Cells
The relationship between Cannabidiol and CB2 receptors in immune cells is a vital part of its mechanism. CBD's interaction with CB2 receptors presents a means of fine-tuning immune responses and inflammation, offering a potential avenue for addressing conditions marked by chronic inflammation and autoimmune disorders.
CBD and Anxiolytic Properties
Anxiolytic Potential
CBD's anxiolytic potential is a compelling area of study. By engaging with the ECS and serotonin receptors, Cannabidiol alleviates symptoms of anxiety disorders. Clinical studies indicate its efficacy, though further research is warranted to unravel the full scope of its anxiolytic properties.
Analgesic Effects and Pain Management
Targeting Pain Pathways
Pain, an intricate interplay of signals, can find relief through CBD's multi-faceted approach. By influencing CB1 receptors and activating the TRPV1 receptor, Cannabidiol offers a multifunctional strategy for managing pain. Comparative studies with traditional pain medications highlight CBD's promise as a natural analgesic.
Bioavailability and Administration Methods
Maximizing Cannabidiol Absorption
The journey of CBD within the body is influenced by its bioavailability—the amount that enters the bloodstream. Different administration methods—oral ingestion, sublingual application, topical use, and inhalation—affect the speed and efficiency of Cannabidiol absorption, determining how quickly its effects are felt.
Safety, Side Effects, and Future Research
CBD's Safety Profile
CBD's safety profile is notable, with few severe side effects reported. Most users experience mild, temporary effects such as fatigue, diarrhea, or changes in appetite. However, it's crucial to exercise caution, particularly if using Cannabidiol alongside other medications.
Ongoing Research and Potential
The exploration of CBD's mechanism is an ongoing endeavor. Researchers continue to uncover new receptors and pathways influenced by Cannabidiol. As science advances, we can anticipate further revelations, expanding the horizons of Cannabidiol-based therapies and wellness strategies.
Conclusion
In the world of wellness and therapeutic potential, Cannabidiol emerges as a multifaceted gem. Its mechanism of action, intricately woven into the fabric of the endocannabinoid system and beyond, offers a profound understanding of how this compound impacts our bodies. As research persists and knowledge deepens, Cannabidiol's therapeutic applications are poised to usher in a new era of healthcare—a realm where science and nature intertwine for the betterment of human well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is CBD the same as THC?
CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) are both compounds found in cannabis plants, but they have distinct effects. Unlike THC, Cannabidiol is non-intoxicating and does not produce a “high.”
How does Cannabidiol interact with the endocannabinoid system?
It interacts with the endocannabinoid system by modulating CB1 and CB2 receptors. It influences various physiological processes, such as mood, pain perception, and immune responses.
What are CB1 and CB2 receptors?
CB1 receptors are primarily located in the brain and central nervous system, influencing functions like memory and pain. CB2 receptors are found in immune cells and play a role in inflammation regulation.
Does CBD directly bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors?
Unlike THC, Cannabidiol does not directly bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors. Instead, it modulates their activity and affects other receptor systems, such as serotonin receptors.
Can Cannabidiol help with anxiety?
CBD's interaction with the endocannabinoid system and serotonin receptors suggests potential anxiolytic effects. Some studies indicate its usefulness in managing anxiety disorders, but more research is needed.
Does CBD have pain-relieving properties?
Yes, CBD has analgesic effects. It influences pain perception through CB1 receptors and activates the TRPV1 receptor, which plays a role in pain sensation.
What is the entourage effect?
The entourage effect refers to the synergistic interaction between various compounds in the cannabis plant, including Cannabidiol, THC, and other cannabinoids. This interaction enhances the overall therapeutic effects.
How is Cannabidiol metabolized in the body?
CBD is metabolized by enzymes in the liver, mainly by the CYP450 family. It undergoes a process known as “first-pass metabolism” before entering the bloodstream.
Are there any side effects of using Cannabidiol?
Cannabidiol is generally well-tolerated, but some individuals may experience mild side effects such as fatigue, diarrhea, or changes in appetite.
Is CBD legal?
The legal status of CBD varies by country and jurisdiction. In some places, Cannabidiol derived from hemp with low THC content is legal, while in others, it can be regulated or prohibited. It's crucial to know the laws in your region.

Nutritionist
Milena Kaler, a skilled nutritionist, enhances the accuracy and comprehensiveness of our supplement reviews.










+ There are no comments
Add yours