“CBD, short for cannabidiol, has become incredibly popular in wellness circles. But there's one question that often confuses people: Does CBD get you high? Let's explore the science behind it and get a clear answer. CBD is known for its non-psychoactive properties, meaning it won't alter your state of mind or create a ‘high.' In this brief journey, we'll unravel the facts, so you can understand why CBD is all about wellness without the high.”
Table of Contents [show]
Understanding CBD and THC
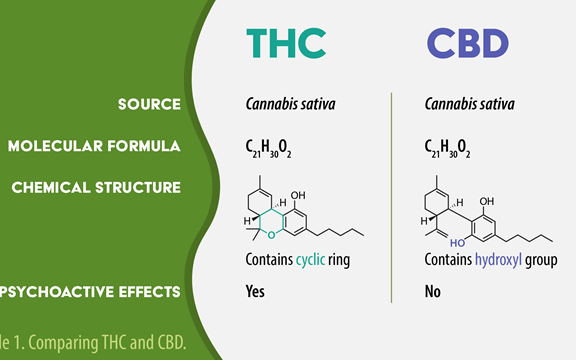
To grasp the answer, we need to understand two key compounds found in cannabis: CBD and THC. While they share the same plant origin, they have vastly different effects.
- CBD (Cannabidiol): CBD is a non-psychoactive compound, meaning it won't alter your state of mind or create a “high.” Instead, it interacts with your body's endocannabinoid system to potentially deliver various health benefits.
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol): THC is the psychoactive component responsible for the characteristic “high” associated with cannabis. It binds to certain receptors in the brain, altering perception, mood, and consciousness.
The Science Behind Getting High
THC achieves its psychoactive effects by binding directly to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system. This interaction triggers the release of dopamine and other neurotransmitters, leading to altered perceptions and sensations.
CBD: Non-Psychoactive Nature
Now, let's address the central question: Does CBD get you high? The answer is a resounding no. CBD doesn't bind strongly to the same receptors as THC, and it doesn't produce the intoxicating effects associated with getting high. Instead, CBD influences the endocannabinoid system in a way that promote relaxation, reduce anxiety, relieve pain, and improve sleep—all without the mind-altering experience.
Does CBD Get You High?
To comprehend why CBD doesn't induce a high, it's crucial to grasp the mechanics of what gets us high in the first place. This sensation primarily stems from a compound called THC, short for tetrahydrocannabinol, found in marijuana. THC is what attaches to specific receptors in the brain known as cannabinoid receptors, primarily CB1 receptors.
When THC connects with these receptors, it triggers a series of reactions that ultimately lead to the euphoric sensations associated with being high. These reactions include the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter linked to pleasure and reward, and alterations in cognitive functions.
CBD, on the other hand, interacts differently with our endocannabinoid system. It has a low affinity for the CB1 receptors and doesn't bind to them tightly. As a result, it doesn't set off the same chain of events that lead to a high. Instead, CBD subtly influences the endocannabinoid system, potentially offering various health benefits without the psychotropic effects.
In essence, while THC directly activates the receptors responsible for getting you high, CBD takes a more indirect and gentle approach, focusing on promoting balance and well-being within the body. This fundamental difference in how these compounds interact with our biology is the key to understanding why CBD doesn't produce a high, making it a sought-after option for those seeking therapeutic benefits without altered consciousness.
Benefits of CBD
CBD offers a host of potential therapeutic benefits, including:
- Pain Relief: CBD help alleviate various types of pain, from chronic conditions to minor discomfort.
- Stress and Anxiety Reduction: Many individuals use CBD for its calming effects and potential anxiety relief.
- Improved Sleep: CBD can promote relaxation, potentially leading to better sleep quality.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: CBD's anti-inflammatory effects benefit conditions like arthritis and inflammation-related pain.
- Effects on Epilepsy: CBD has received FDA approval as a treatment for specific forms of epilepsy.
Along with the benefits of CBD, there are some common side effects too. You won't suffer much, as it is a minor effect.
Legal Status of CBD
Is CBD legal? It depends on where you live. In the United States, CBD derived from hemp with less than 0.3% THC is federally legal. However, state regulations can vary, so it's crucial to be aware of local laws.
Types of CBD Products
CBD comes in various forms, allowing individuals to choose what works best for them:
- CBD Oil: A versatile option that can be taken under the tongue or added to beverages and food.
- CBD Gummies: Tasty and convenient, these gummies offer a delicious way to consume CBD.
- CBD Capsules: Precisely dosed and easy to swallow, capsules provide no-fuss options.
CBD and Drug Testing
One common concern is whether CBD can cause you to fail a drug test. While pure CBD is unlikely to result in a positive test for THC, it's essential to be cautious when using full-spectrum CBD products. These can contain trace amounts of THC that might accumulate over time.
Does CBD Gummy Bears Show Up on a Drug Test? – Read more
Real-Life Experiences
Let's hear from individuals who have used CBD and can attest to its non-psychoactive nature:
- Kiara's Story: “CBD oil has been a game-changer for my chronic pain. I can finally find relief without feeling high.”
- James' Experience: “I use CBD gummies for anxiety, and they help me stay calm without any mind-altering effects.”
Conclusion
The answer to “Does CBD get you high?” is a definitive no. CBD's non-psychoactive nature sets it apart from THC, making it a promising option for individuals seeking potential health benefits without the intoxicating effects. Whether you choose CBD gummies, oil, or another product, understanding its properties and potential is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between CBD and THC?
CBD and THC are both compounds found in cannabis, but they have different effects. THC is psychoactive and makes you feel high, while CBD is non-psychoactive and won't alter your state of mind.
How does CBD interact with the body's endocannabinoid system?
CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in your body, helping to regulate various functions like pain, mood, and sleep. It doesn't produce a high but offer therapeutic benefits.
Can you get addicted to CBD?
CBD is not considered addictive. It lacks the properties that lead to dependence or cravings like those associated with addictive substances.
What are the potential side effects of CBD?
Common side effects of CBD are mild and include dry mouth, changes in appetite, diarrhea (in rare cases), and fatigue. These effects are generally not severe.
Is it possible to overdose on CBD?
It's challenging to overdose on CBD. Even in high doses, it typically doesn't produce harmful effects. However, using moderate amounts is recommended.
Can CBD interact with other medications?
CBD can interact with some medications, so it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you're taking other medications.
How long does it take for CBD to work?
The time it takes for CBD to work varies depending on the product and your body. Typically, effects be felt within 30 minutes to 2 hours.
Are there age restrictions for buying CBD products?
Age restrictions for purchasing CBD products vary by location. In some places, you must be 18 or 21 years old to buy them legally.
Can you travel with CBD?
Traveling with CBD can be complex due to varying regulations. It's essential to research the laws of your departure and arrival destinations and follow TSA guidelines for air travel.
How can I find high-quality CBD products?
Look for reputable brands that provide third-party lab test results to ensure product quality. Additionally, consider the type of product that suits your needs and preferences.

MD
Dr. Phillips, a board-certified medical doctor (MD) specializing in preventive medicine, provides valuable insights to our supplement review process.











+ There are no comments
Add yours